Resources
What is the Endocannabinoid System, or ECS?
Discovered in the late 1980s, the Endocannabinoid System, or ECS is a biological system found in all mammals, composed of endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors. ECS affects virtually every cell, muscle, organ and tissue in our body, and critical to regulating a wide range of body processes, our nervous system, immune system, digestive system, endocrine glands, brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, spleen, bones, muscles, blood vessels and cells, lymph cells, and fat cells.
The ECS is believed to have more cellular receptor sites than any other receptor system. The widespread distribution of these cannabinoid receptors shows just how important the ECS is to our overall bodily function and health.
The ECS promotes homeostasis, or dynamic biological balance, in every cell, tissue, and organ, including the brain.
What are Endocannabinoids?
Endocannabinoids are endogenous neurotransmitters that are produced by our bodies. They regulate neurotransmission and allow for feedback loops. Anandamide and 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) are the two primary endocannabinoids.
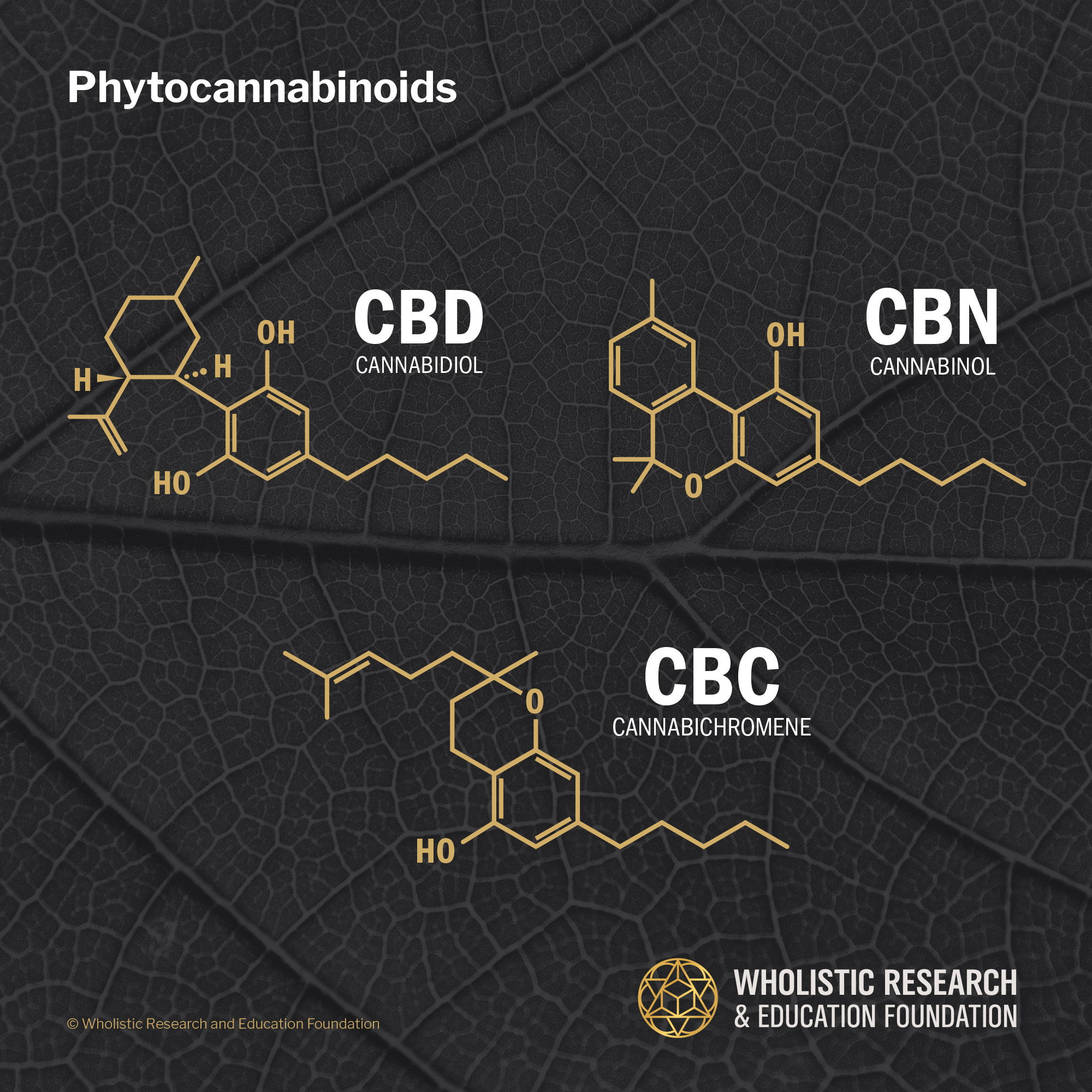
What are Phytocannabinoids and how are they different than Endocannabinoids?
Phytocannabinoids are plant derivative compounds (primarily extracted from cannabis) that mimic the characteristics of the endocannabinoids. THC and Cannabidiol (CBD) are the two primary phytocannabinoids that mimic the endocannabinoids Anandamide and 2-AG, respectively.
Both endocannabinoid and phytocannabinoids, collectively referred to as cannabinoids, bind to cannabinoid receptors that exist throughout the mammalian body.
What are cannabinoid receptors?
Our ECS includes two primary cell cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2. While these receptors are found throughout the body, they tend to concentrate in certain areas. CB1 receptors are abundant in the brain, while CB2 receptors are more often found on immune cells, in the gastrointestinal tract, and in the peripheral nervous system.
The endocannabinoid Anandamide, as well the phytocannabinoid THC target CB1 receptors, predominantly found in the brain and nervous system, as well as in peripheral organs and tissues. The other main endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and its own mimetic phytocannabinoid, CBD, are active at both CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors.
Why is ECS important?
There is increasing data that the endocannabinoid system plays an integral role in our overall physical and psychological wellness by promoting homeostasis. Specifically, both 2-AG and CBD are involved in the regulation of immune system functions, inflammation, sleep, stress response, appetite, mood, memory and pain management.
While CBD is not yet FDA approved for any condition (with the notable exception of the recent approval of Epidiolex™ as anti-seizure medication), many studies have shown promising results for a variety of conditions. Indications are that CBD:
- Combats anxiety and depression
- Combats inflammatory disorders
- Reduces nausea and vomiting
- Suppresses seizure activity
- Combats psychiatric disorders
- Combats neuro-generative discovers
- Combats tumor or cancer cell growth